Data Security Assessment: Strengthening Your Organization’s Defenses
Data Security Assessment: Strengthening Your Organization’s Defenses
Blog Article
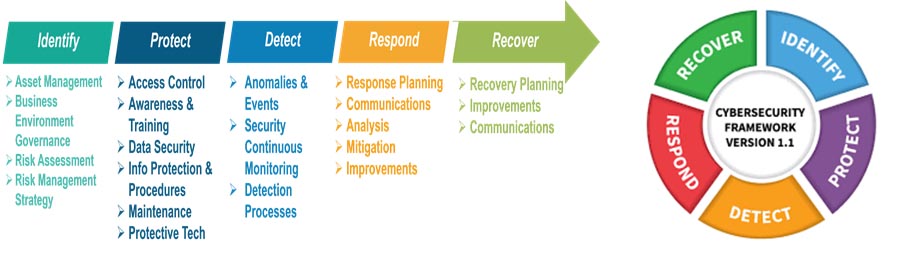
In an era where cyber threats are becoming more sophisticated and frequent, ensuring the security of your organization’s data is critical. From sensitive customer information to intellectual property and financial records, data is a valuable asset, and its protection is a top priority for businesses of all sizes. One of the most effective ways to assess and enhance the security of your organization’s data is through a Data Security Assessment (DSA).
A Data Security Assessment is a structured evaluation process that involves identifying, analyzing, and mitigating security risks related to an organization’s data. The goal is to identify potential vulnerabilities in data protection measures, ensure compliance with data protection laws, and improve overall security posture to prevent data breaches and unauthorized access.
In this article, we will explore what a Data Security Assessment is, why it is crucial for your organization, the key components of a DSA, and how businesses can conduct one to enhance data security.
What is a Data Security Assessment?
A Data Security Assessment is an evaluation of an organization’s data protection policies, controls, and processes to determine how effectively they are securing sensitive data. This assessment examines all aspects of data security, including access controls, encryption, data storage, data handling, and employee practices. It also looks at how the organization complies with relevant data protection regulations, such as GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS.
The goal of a DSA is to identify potential security gaps, assess the risks associated with data breaches, and provide actionable recommendations for improving data protection measures. By conducting regular DSAs, organizations can ensure that their data security practices remain strong, evolving, and capable of defending against emerging threats.
Why is a Data Security Assessment Important?
- Identify Security Gaps and Vulnerabilities: A DSA helps organizations identify weaknesses in their data security framework. By pinpointing areas of vulnerability—such as outdated security protocols, improper data handling procedures, or insufficient encryption—organizations can take corrective action before an attack or breach occurs.
- Ensure Compliance with Data Protection Regulations: With the introduction of stringent data privacy regulations worldwide, businesses must ensure their data security practices are compliant with laws like GDPR in Europe, CCPA in California, and HIPAA in the healthcare sector. A DSA evaluates whether the organization is meeting these compliance standards and highlights areas that require improvement to avoid penalties or fines.
- Mitigate Risks of Data Breaches: Data breaches can lead to significant financial, reputational, and legal consequences for organizations. By conducting a DSA, businesses can proactively address risks, such as unauthorized access, data loss, or insider threats, thereby reducing the likelihood of a breach.
- Strengthen Internal Security Measures: Regularly assessing data security allows organizations to stay ahead of emerging threats and adopt industry best practices. This can involve updating security tools, enforcing stricter access controls, implementing robust encryption standards, and enhancing employee training on data security protocols.
- Protect Sensitive Data: Data is the lifeblood of modern organizations, and sensitive data—such as personal identifiable information (PII), financial records, or intellectual property—must be protected at all costs. A DSA helps ensure that sensitive data is adequately safeguarded against threats, reducing the risk of exposure or theft.
- Increase Customer and Stakeholder Trust: By demonstrating a commitment to securing customer data, businesses can build trust with clients, customers, and stakeholders. Regular DSAs and clear data protection measures show that the organization values privacy and takes data security seriously.
Key Components of a Data Security Assessment
- Data Inventory and Classification: The first step in a DSA is identifying and classifying the types of data the organization handles. This includes customer data, employee data, financial information, intellectual property, and any other sensitive or confidential data. Classifying data based on its sensitivity helps determine the level of protection required for each type of data.
- Access Control and Authentication: Access control is a critical component of data security. A DSA evaluates how access to sensitive data is granted, monitored, and revoked. This involves reviewing user permissions, roles, and whether multi-factor authentication (MFA) is used. Ensuring that only authorized personnel have access to sensitive data is vital to preventing unauthorized access and insider threats.
- Encryption and Data Masking: A DSA assesses whether sensitive data is encrypted both at rest (when stored) and in transit (when transmitted over networks). Encryption is a fundamental tool for protecting data, ensuring that even if data is intercepted or accessed by unauthorized individuals, it cannot be read without the decryption key. Data masking may also be used to obfuscate sensitive data, ensuring that only authorized users can view it in full.
- Data Storage and Backup: A Data Security Assessment looks at how and where sensitive data is stored. This includes evaluating whether data is securely stored in physical and cloud environments, whether backup systems are in place, and whether those backups are properly protected and regularly tested.
- Data Handling and Disposal: Proper handling and disposal of data are essential to preventing unauthorized access. A DSA evaluates how data is collected, processed, shared, and deleted. This includes ensuring that sensitive data is not inadvertently shared with unauthorized parties and that data is securely disposed of when it is no longer needed.
- Incident Response and Data Breach Preparedness: A critical aspect of a Data Security Assessment is evaluating how well an organization is prepared to respond to data breaches or security incidents. This includes reviewing the incident response plan (IRP), how quickly breaches can be detected, how they are communicated internally and externally, and whether there are clear procedures for mitigating damage.
- Third-Party Risk Management: Many organizations rely on third-party vendors or service providers to manage certain data or systems. A DSA evaluates the security practices of these third-party vendors, ensuring that they meet the same security standards as the organization and that contracts and agreements include data protection clauses.
- Security Awareness and Employee Training: Human error remains one of the most common causes of data breaches. A DSA assesses whether employees are properly trained in data security best practices, including recognizing phishing attacks, handling sensitive data responsibly, and following security protocols. Regular training and awareness programs are essential for mitigating risks associated with human error.
Steps to Conduct a Data Security Assessment
- Define the Scope: Determine the scope of the assessment, including which departments, systems, or data will be included. It’s important to prioritize high-risk areas, such as sensitive customer data, financial records, and intellectual property.
- Conduct a Data Inventory: Identify and classify all the data assets that the organization handles. This process helps determine where sensitive data resides and how it is managed.
- Evaluate Security Controls: Review the current security measures in place, including encryption, access control, and incident response procedures. This step identifies any weaknesses or areas where improvements are needed.
- Assess Compliance: Evaluate whether the organization’s data security practices comply with relevant laws and regulations, such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI-DSS. Non-compliance can lead to legal penalties and reputational damage.
- Identify Risks and Vulnerabilities: Use the information gathered during the assessment to identify potential risks, such as weak access controls, outdated software, or insecure data storage. A thorough risk assessment helps prioritize which vulnerabilities need to be addressed first.
- Implement Recommendations: Based on the findings of the assessment, implement security improvements. This may include updating security policies, adopting new technologies, enhancing employee training, or strengthening third-party security measures.
- Monitor and Review: Data security is an ongoing process. Regular monitoring, audits, and periodic DSAs ensure that your data protection measures remain effective and can adapt to emerging threats.
Benefits of a Data Security Assessment
- Enhanced Data Protection: A DSA helps identify weaknesses in data security practices, allowing organizations to implement stronger protections and reduce the risk of data breaches.
- Regulatory Compliance: By ensuring compliance with data protection laws, organizations avoid penalties and legal issues, while also safeguarding customer privacy.
- Reduced Risk of Data Breaches: By identifying and mitigating risks before they lead to a breach, a DSA helps reduce the likelihood of costly data breaches and reputational damage.
- Improved Security Posture: Regular data security assessments help organizations stay ahead of evolving cyber threats by ensuring that their security measures are up to date and robust.
- Increased Trust: Demonstrating a commitment to data security enhances customer trust, strengthens business relationships, and improves the organization’s reputation.
Conclusion
A Data Security Assessment is a vital process for any organization seeking to protect sensitive data from cyber threats and regulatory risks. By identifying vulnerabilities, ensuring compliance with laws, and implementing best practices, businesses can safeguard their data, mitigate risks, and build trust with customers and stakeholders. Regular DSAs ensure that data protection measures remain effective in a constantly evolving threat landscape, ultimately contributing to the long-term success and security of the organization. Report this page